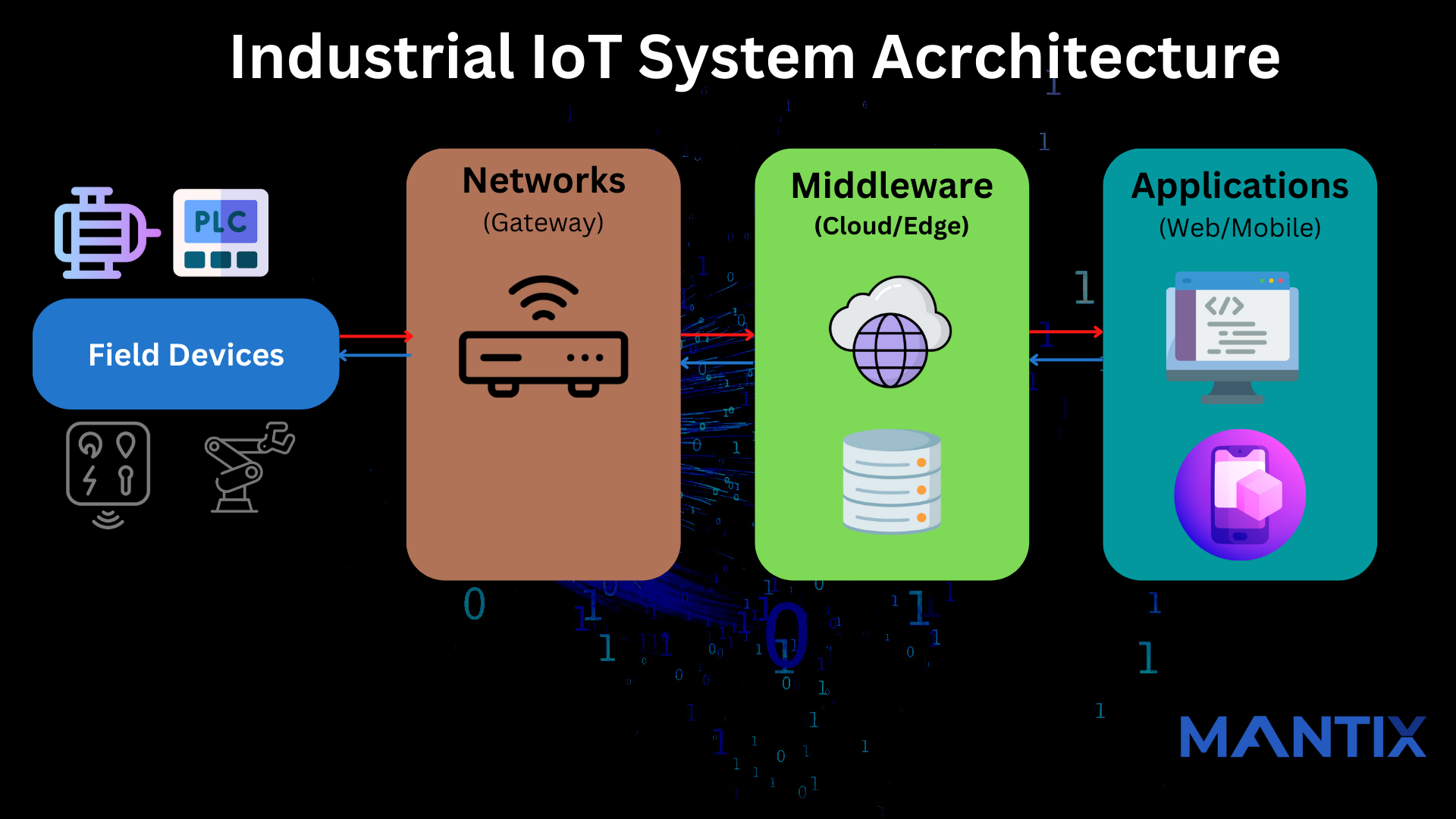
Field Devices: Sensors and field devices are used in data acquisition to measure physical conditions of a machine. They consist of devices that receives or measures inputs and outputs that performs an action. This data can be used to trigger a machine response, or it can be used to collect data for analysis and storage. Field devices in Manufacturing Industry are Sensors, Motors, Electrical Systems, Switches, Controllers, PLC’s, HMI, VFD, Servo, Robots, Actuators, Relays, Indicators & more…
Networks (Gateway): Industrial IoT gateway is a device that serves as a bridge between industrial devices and the internet. It enables the data collection and transmission of industrial devices, such as sensors and controllers, to cloud-based systems for analysis and control. It also allows for remote monitoring and management of industrial equipment. The gateway typically includes features such as communication protocols, data processing, and security to enable communication between the industrial equipment and the internet.
- Typical Data Acquisition Protocols (Downstream) supported by Industrial IoT Gateways are OPC, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRa, BAcnet, Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, Uni-Telway, EtherNet/IP, DF1, FINS TCP, FINS Hostlink, ISO TCP, PPI, MPI, Profibus, Mitsubishi FX, Hitachi EH, ASCII & more.
- IoT Connectivity i.e., Data Publishing Protocols (Upstream) supported by Industrial IoT Gateways are MQTT, SNMP, HTTPs, CoAP, OPC UA & more.
Middleware (Cloud/Edge): Industrial IoT middleware system having two options available to the customer those are Cloud and Edge Computing Platforms.
- Cloud computing allows users to access these resources on-demand, without the need for them to own or maintain the underlying infrastructure. This can provide benefits such as increased scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
There are several types of cloud computing services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Cloud having Public and Private Options, public clouds are shared resources and can be accessed by anyone over the internet while private clouds are dedicated resources, usually owned by a specific organization and accessed over a private network.
- Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices or “edges” of a network. The goal of edge computing is to reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing, storage, and analysis, and to enable real-time decision making and low-latency applications. By processing data at the edge, edge computing can also help reduce costs associated with data storage and transmission
Applications (Web/Mobile): Software application performs wide range of tasks like processing, analysis and user-friendly interface with customer for taking inputs and display results. applications can be accessed via web browsers on desktop computers or mobile devices, and they provide a user-friendly interface for controlling, monitoring, and interacting with IoT devices.
- Web Applications – IoT web applications are typically accessed via a web browser and can be used to monitor and control IoT devices, view sensor data, and receive notifications and alerts. They can also provide historical data and analytics and allow for the configuration and management of IoT devices.
- Mobile Applications – IoT mobile applications, on the other hand, are designed for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets and provide similar functionality as IoT web applications. They allow users to access and control IoT devices, view sensor data, and receive notifications and alerts from anywhere using their mobile devices. They can also provide location-based services, and can work offline if the device is disconnected from the internet.